Overview
We have had a few projects on Sitecore JSS where we needed to implement search. These projects followed Helix principles and were heavily component based. I generally found there were not many examples on implementing cross cutting search in the community. I want to share our take on implementing search in Sitecore JSS while following Helix principles.
All of the examples provided were written for Sitecore 9.3.
This post is part 1 of a multi part series. Part 1 provides the high level design of the supporting search API. Part 2 will cover how this plays into JSS. Part 3 will include example source code.
Requirements
To set the stage, I want to talk about the requirements that we needed to meet when building out search support. The sites we were implementing had similar requirements for search. Each site had section searches and an overall site search. There are also searches performed behind the scenes to look up relationships. These searches were to be powered by Solr. Here are a few mockups to better explain the general search requirements. These are abbreviated requirements for this blog post.
Search Screens
Here are the requirements for search pages with results. There are typically more search pages in a site than this, but we will only focus on People Search, Insights Search, and Site Search.
People Search
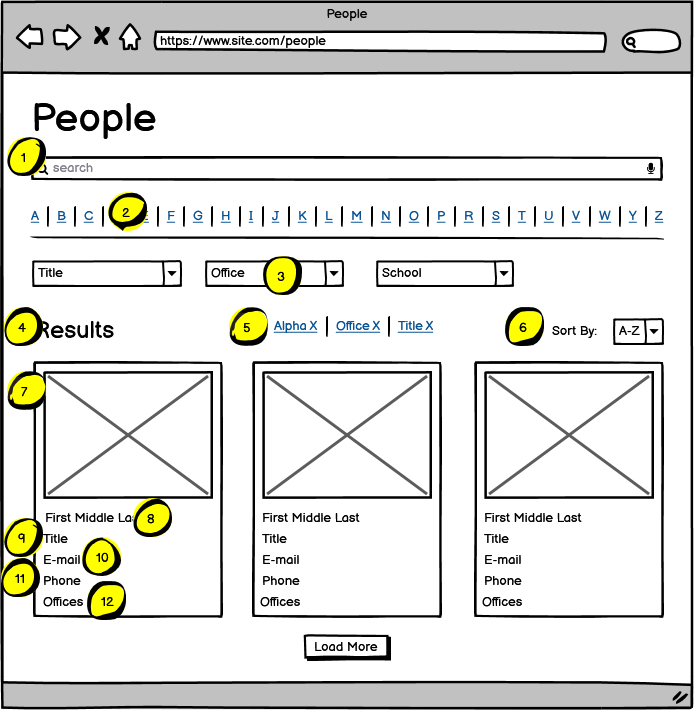
| Name | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | People Keyword Search | Search field: Performs a starts with on First and Last names |
| 2 | Alpha-Select Search | Alpha-select search: Allows users to search for professionals by the first letter of their last name. Element includes A to Z links, only letters with corresponding results will be enabled for selection. |
| 3 | Search Drop-down Filters | All filters are single-select filters, one selection per filter can be applied per search. Selection of any filter will execute a search and refresh the page and append the filter to the Applied Filters. Only the options with corresponding results will display. This rule applies with multiple filters. Filters will function as an “AND” search when multiple filters are selected. |
| 4 | People Results Listing | Search results will display on the page. On initial load, 16 People Result Cards will display. Number of items displayed is editable by content editor and will be used for both the initial results listing and the selection of the “Load more” link. |
| 5 | Applied Filters | On select of drop down filter selections, corresponding applied filter chips are displayed. Clicking the “x” icon corresponding to any applied filter chip will clear the filter and refresh the search results accordingly. |
| 6 | Sort Controls | Dropdown Sort Selections include: A-Z (selected by default), Z-A |
| 7 | Image | Thumbnail image of person. On click, user is directed to the corresponding People Detail page. |
| 8 | Display Name | Displays corresponding People name. On click, user is directed to the corresponding People Detail page. |
| 9 | Title | Displays title field if entered. |
| 10 | On click, user’s default email application is launched with the TO field pre-populated with the corresponding person’s e-mail address. | |
| 11 | Telephone | Displays phone number associated with the corresponding professional, launches user’s native phone application with the number pre-dialed. |
| 12 | Offices | Offices associated with a person will display. |
Insights Search

| Name | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Insights Keyword Search | Search field: user can enter a query into the field. The following fields will be searched: Title, Abstract, body content fields (e.g., anything entered in rich text fields). |
| 2 | Search Drop-down Filters | All filters are single-select filters, one selection per filter can be applied per search. Selection of any filter will execute a search and refresh the page and append the filter to the Applied Filters. Only the options with corresponding results will display. This rule applies with multiple filters. Filters will function as an “AND” search when multiple filters are selected. |
| 3 | Applied Filters | On select of drop down filter selections, corresponding applied filter chips are displayed. Clicking the “x” icon corresponding to any applied filter chip will clear the filter and refresh the search results accordingly. |
| 4 | Search Results Listing | On initial load, 10 search results will display. Number of items displayed is editable by content editor and will be used for both the initial results listing and the selection of the “Load more” link. Results are ordered by date descending. |
Site Search
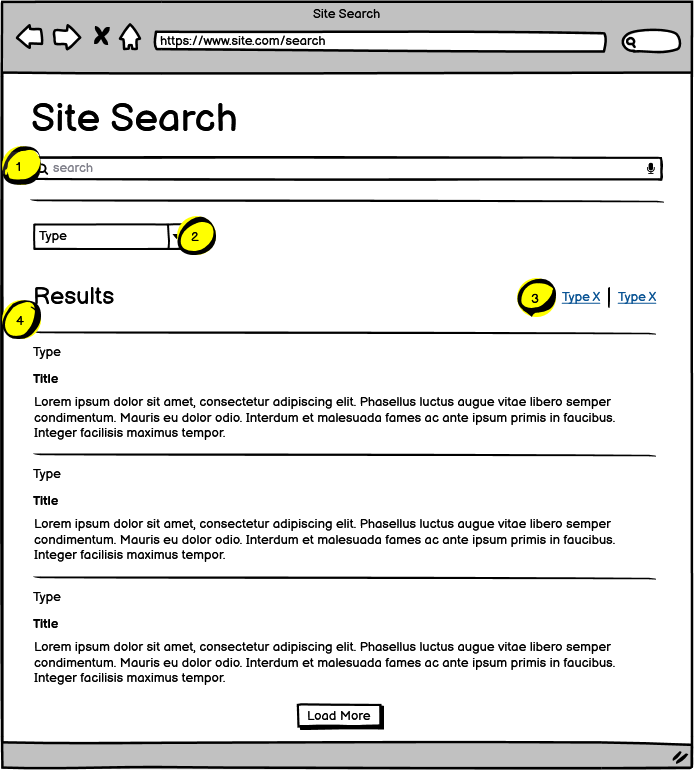
| Name | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Keyword Search Bar | The site search field is used to conduct a keyword search across all website content |
| 2 | Search Drop-down Filters | All filters are single-select filters, one selection per filter can be applied per search. Selection of any filter will execute a search and refresh the page and append the filter to the Applied Filters. Only the options with corresponding results will display. This rule applies with multiple filters. Filters will function as an “AND” search when multiple filters are selected. |
| 3 | Applied Filters | On select of drop down filter selections, corresponding applied filter chips are displayed. Clicking the “x” icon corresponding to any applied filter chip will clear the filter and refresh the search results accordingly. |
| 4 | Search Results Listing | On initial load, 10 search results will display. Number of items displayed is editable by content editor and will be used for both the initial results listing and the selection of the “Load more” link. The results are ordered by relevance |
Relationship Search
When you think of search, you typically think of search criteria pages with associated results. Sometimes search is needed to look up and display related data on pages. For example, contacts can be added to insight detail pages. There may be a requirement to display what insights a person is related to on a person detail page. Below are 2 sample detail page designs that impact relationship searches.
People Detail
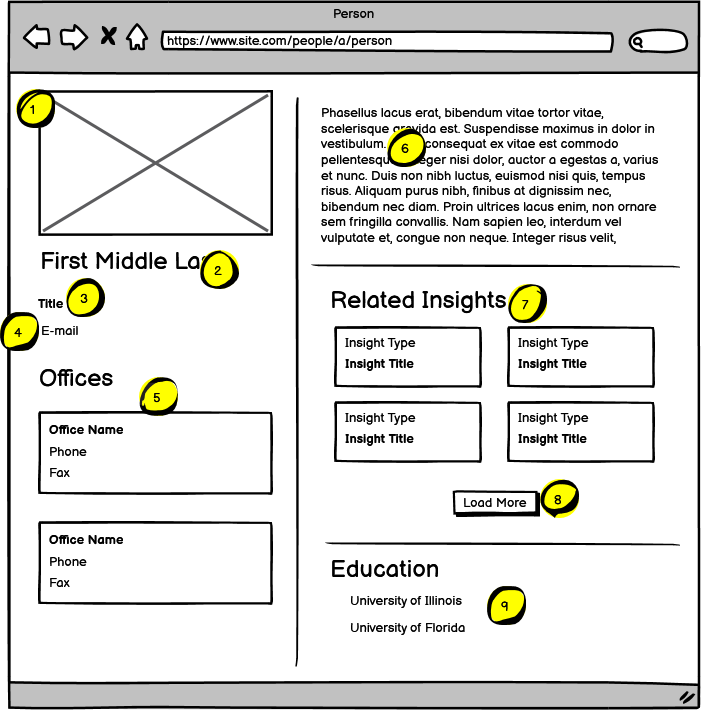
| Name | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | People Photo | Displays first name, middle initial, last name by default. |
| 2 | Name | Displays title as selected by content editor. Single select from list of defined titles. |
| 3 | Title | Displays title as selected by content editor. Single select from list of defined titles. |
| 4 | Displays e-mail address for the corresponding person. Launches user’s default email application with the TO field pre-populated. | |
| 5 | Office Listings | Up to 4 offices may be selected, linking to corresponding office detail page. |
| 6 | Bio Copy | This is rich text content |
| 7 | Related Insights | Displays 4 most recent Insights items tagged to the person. Content editor may pin specific Insights items for priority order on the grid. Any additional items will be displayed in reverse chronological order. |
| 8 | Show More Button | If more than 4 Insights are associated with a person, the Show More button appears. On click, an additional 4 items appear. Show More button appears until all Related Items are loaded. |
| 9 | Education | Displays a list of related schools. Schools are selected from a defined list of schools |
Insight Detail
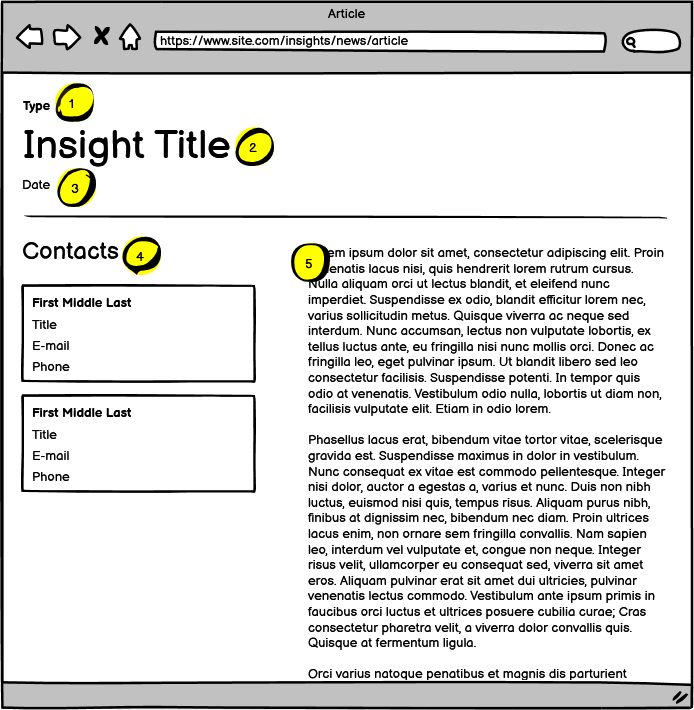
| Name | Notes | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Insight Type | The type of insight. This value comes from a lookup list of insight types. |
| 2 | Title | The title of the insight. |
| 3 | Date | The date of the insight. |
| 4 | Contacts | The list of contacts related to the insight. This is a multiselect that relates to people. |
| 5 | Body Copy | This is rich text content |
Office Detail
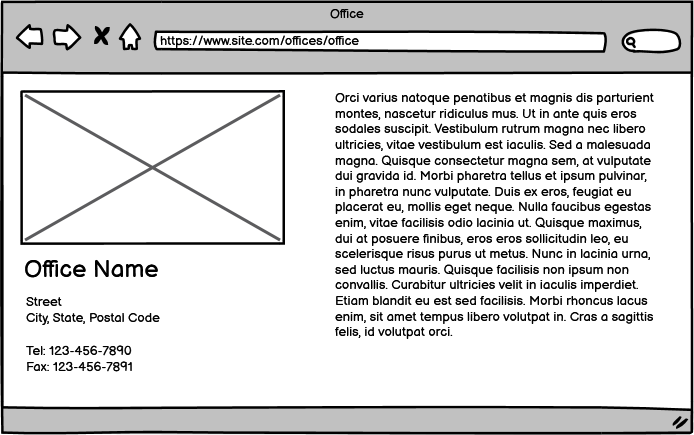
For offices, I am really just calling out that it exists. I will not list out the requirements.
High Level Design
Now that we have the requirements from above, we can start the high level design. Before starting the implementation, we can break out the requirements.
Search
Let’s break out the search requirements. We will list the filters, queries, and sort fields
| Page / Component | Filter/Facet Fields | Query Fields | Sort By Fields |
|---|---|---|---|
| Related Insights | Insight - Contacts | - | Insight - Date |
| People Search | People - Last Name Letter People - Title Office - ID School - ID |
People - First Name People - Last Name |
People - Last Name |
| Insights Search | Insight - Type | Insight - Title Rich Text Content |
Insight - Date |
| Site Search | Insight - Type People - Title |
People - First and Last Name Insight - Title, Rich Text Content |
Relevance |
As described in the requirements, the drop down filters only display the available criteria. This means that only the offices that people are related to will be displayed. As additional filters are added, the available criteria is further filtered. We can use Facets in Solr to return the how many items in the index are using a criteria item. This will allow us to only display criteria that have results. All of the filter fields will be used as facets except “Insight - Contacts.”
Each section uses different fields for the search. Some of the fields can be treated as the same across all searches. Site search spans across all sections. Section searches are a bit more isolated, but still share some of the same functionality.
Helix
How does this fit into Helix?
According to Helix principles, the functionality would most likely be broken out into the following Feature Modules. Because there similarities between each of the modules, the common logic should go into a foundation module.
- Feature
- People
- Insights
- Search (site search)
- Foundation
- Search
Keep in mind that feature modules are not allowed to reference each other. They cannot know each other exist. They can only reference Foundation modules.
Components / Renderings
We want to break apart the pages into separate components / renderings. A benefit of breaking pages into components is to allow flexibility in laying out pages. Content managers can re-arrange components in the page editor. Components also allow for personalization and A/B testing. Another benefit of components is they allow breaking apart functionality into Helix features, keeping the logic contained within their respective modules.
Lets break apart the detail pages, calling out what Helix module the components should belong to.
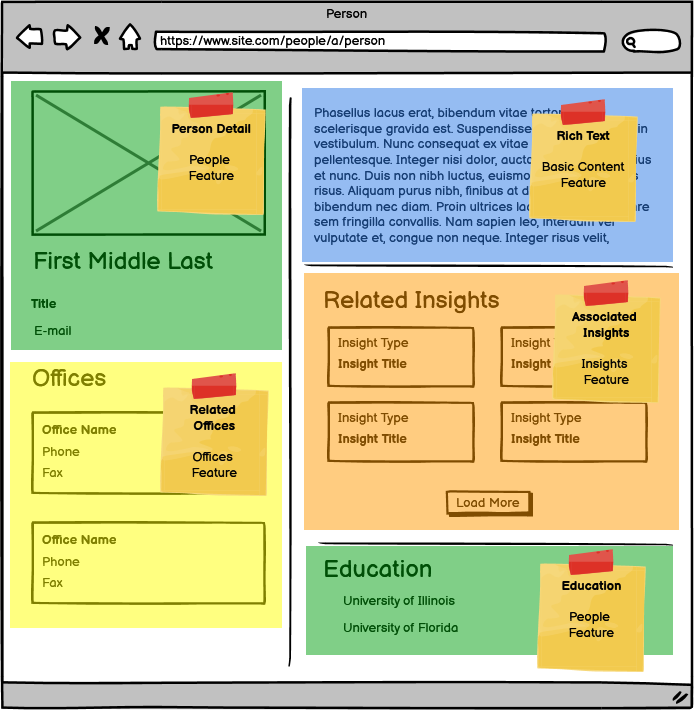
People Detail results in 5 components:
- Person Detail from the People Feature
- Related Offices from the Office Feature
- Rich Text from the Basic Content Feature
- Related Insights from the Insights Feature
- Education from the People Feature
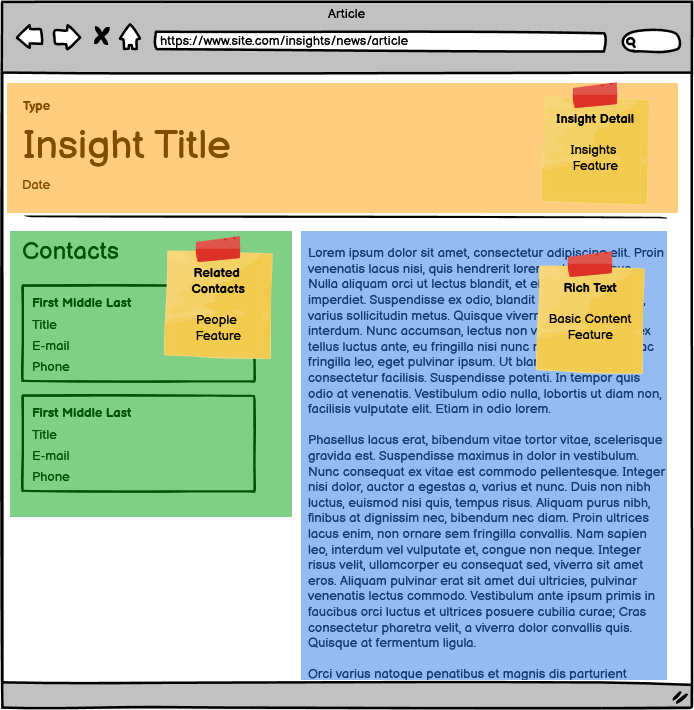
Insight Detail results in 3 components:
- Insight Detail from the Insights Feature
- Related Contacts from the People Feature
- Rich Text from the Basic Content Feature
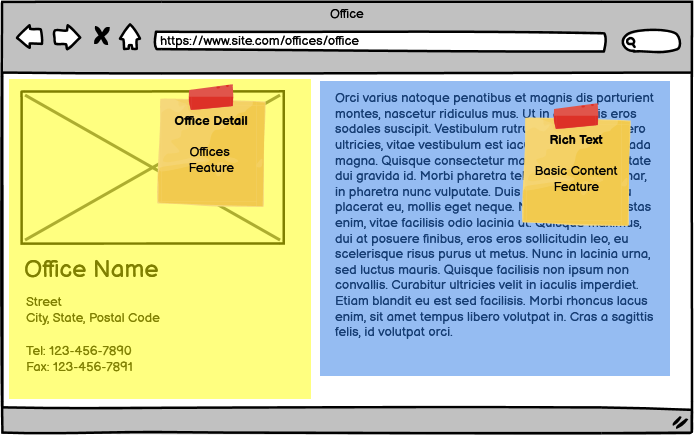
Office Detail results in 2 components:
- Office Detail from the Offices Feature
- Rich Text from the Basic Content Feature
The above examples are very cleanly separated. There is no overlap between the Features.
Now let’s break apart the search pages. The layout of the search is pretty fixed. Content administrators should never have the need to re-arrange components related to search. There are also no requirements around personalization or A/B testing in this case. We can get away with a single search component for each of the pages.
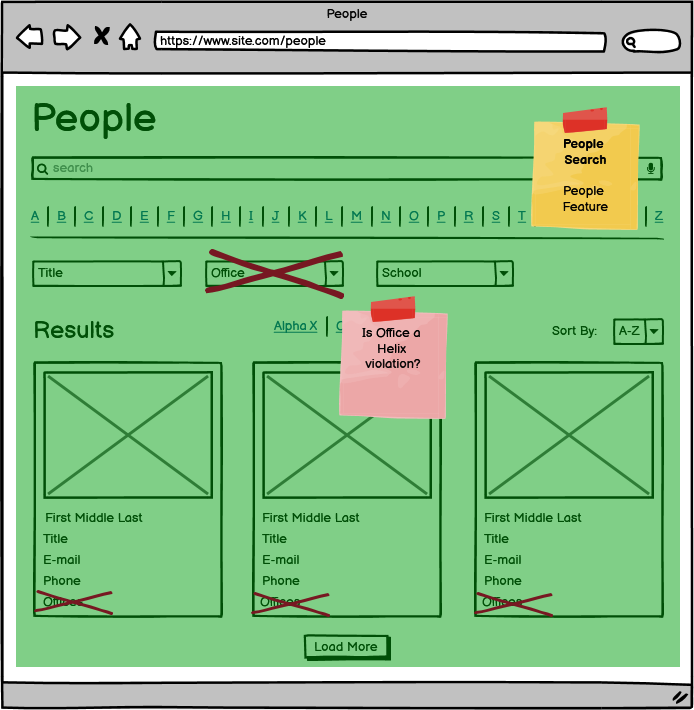
There are potential helix violations in the people search. The People Feature owns this component, but there are references to offices in 2 places. People should not know about offices. We must design around this without violating Helix.
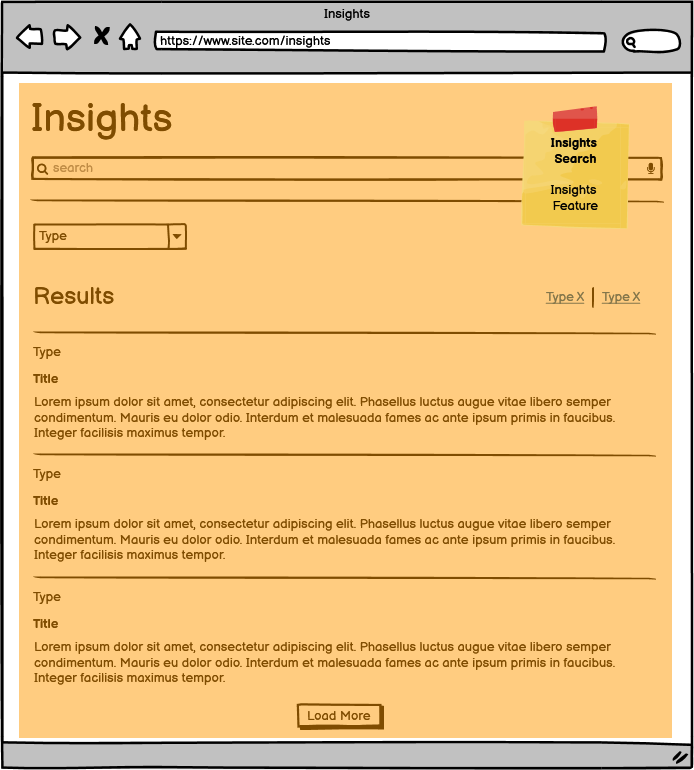
The Insights Search does not have any potential Helix violations. All content and criteria originate from the Insights Feature.
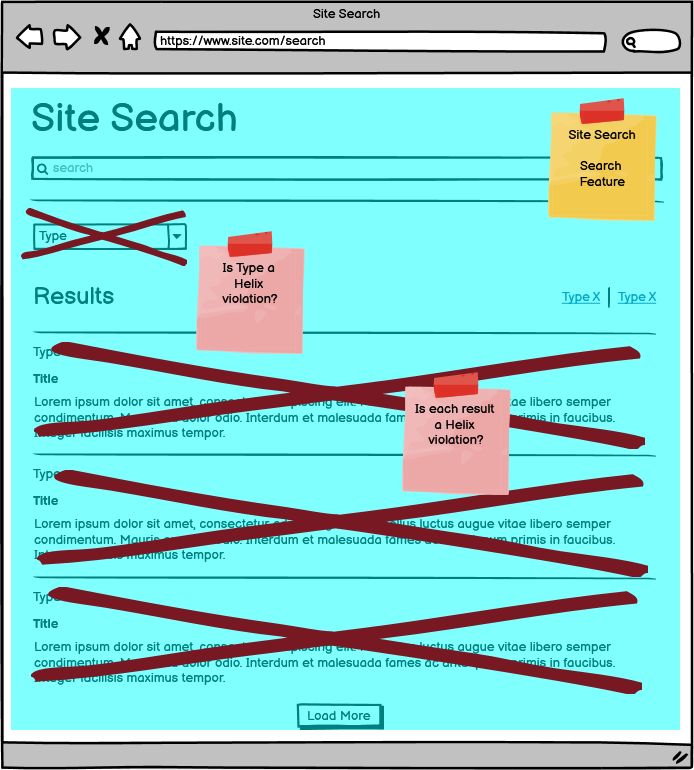
There are potential Helix violations in the site search. The Search Feature owns this component, but there are references to People Titles and Insight Types. The result items are from People, Insights and Offices. Site Search should not know about the People, Insights, and Offices Features. We must design around this without violating Helix.
Providers
Let’s come up with an architecture that does not violate any Helix design principles. We want to split the logic into foundation and feature modules.
Sitecore supports the concept of a Provider framework.
A provider is a component that implements logic. They are used to encapsulate functionality for a problem domain. Much of Sitecore’s functionality is implemented in providers. For example, when you publish items Sitecore uses a publishing provider. Reference
We can use providers as a way for Feature Modules to provide the implementation of the search logic that the Foundation Module needs. Below is a diagram that indicates how this can work.
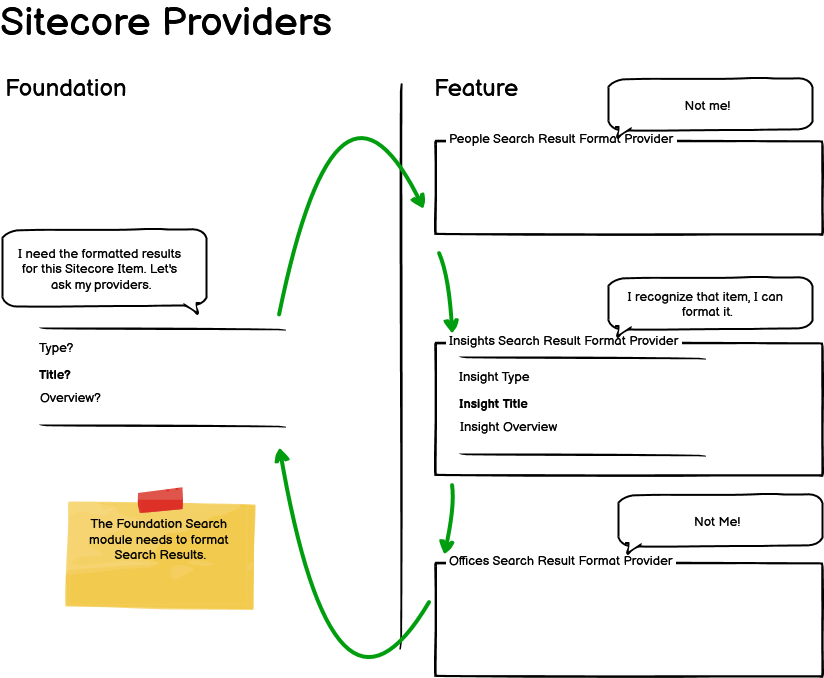
In the case where the site search needs formatted results, we can use providers to provide the formatting of the results. The providers are implemented in the Feature Layer and the interfaces are defined in the Foundation Layer. The implemented providers are then registered via configuration. The logic in the foundation layer can get the registered providers from the configuration. It can then ask each provider for formatted results. The foundation can then use the formatted results from the provider that provides it. The foundation layer does not know about the implementations, it just uses the results from the implemention.
The concept of providers can applied anywhere Features need to own the logic and the Foundation uses the results.
We can break down the required search providers as follows:
| Name | Notes |
|---|---|
| Criteria Provider | This formats and provides the content for the single select drop downs. This solves the problem of the People Search screen needing to display a list of formatted Offices. The office criteria provider will provide the format for the list of offices. Note: the actual list of offices comes from Solr facets, this just formats them. |
| Indexing Provider | This provides values for Computed Fields. Site search requires filtering based on type. The people feature can provide the people types (Partner, Associate, etc.). The insights feature can provide the insight types (Event, News, Publication, etc.) |
| Result Provider | This provider ultimately formats the site search results. Each feature can provide the format of the data it knows how to manage. This solves the problem of the Search Feature not knowing how to format the other feature module’s results. |
| Search Provider | This provider provides the implementation of feature specific search requirements. The shared search logic is in the foundation layer. |
Index design
For performance reasons, we have always created a custom index for the website. This allows us to specify exactly the templates and fields that are to be indexed.
From the designs above, the fields we want to index are as follows:
| Name | Type | Owner | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| local_datasource_content | text | Foundation | Finds all rich text fields that are on the datasources of the components. This automatically discovers the text content to index. |
| templates | stringCollection | Foundation | Includes all templates for an item. This allows feature searches to filter on the base templates defined in the feature |
| alphasort | string | Foundation | Used to enable sorting based on alpha order. Primarily used in People Search |
| associations | stringCollection | Foundation | Stores relationships between features. An insight would have related contacts in this field. |
| datesort | datetime | Foundation | Used to enable sorting based on date. Primarily used in Insights Search |
| contenttype | stringCollection | Foundation | Used to filter and facet on content type for site search |
| title | text | Foundation | Used for keyword search on site search and insight search. Title can be boosted independently from other content |
| offices_offices | stringCollection | Offices | Supports filtering and faceting on offices. |
| people_firstname | string | People | Supports starts with match on people first name. |
| people_lastname | string | People | Supports starts with match on people last name. |
| people_lastnameletter | string | People | Supports filtering and faceting on last name alpha letter |
| people_schools | stringCollection | People | Supports filtering and faceting on schools |
| people_title | string | People | Supports filtering and faceting on people titles |
The owner indicates if the Foundation Search module owns the computed field or the respective Feature module. If the Foundation owns the computed field, the Feature modules will need to provide the value through the provider framework. If the Feature Module owns the field, the Feature Module will need to provide the search implementation through the search provider.
Search Queries, Filters, Facets and Sorting
Let’s address the API that will be used to execute the searches. Recall that the people search has a filter for offices. The people search is being built as one component. It is not composed of other components. Because of this, the people feature needs to know how to include the offices filter. Remember, the people feature cannot be aware of the Offices feature. It can only be aware of the search in the foundation. This pushes us to put the cross cutting filters in the foundation. This way all feature modules have access to any cross cutting filter without needing to reference another feature, causing a Helix violation. The foundation will define these filters, it will not provide the implementation for the feature modules specific filters. The implementation will reside in the respective feature modules. Only the filters owned by the foundation modules will be implemented in foundation.
Here are the available queries, filters, facets, and sort as defined in the foundation module.
SearchFilter:
| Name | Implemented In | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| string Query | All | This is the text query. Each module defines what fields are searched. |
| ICollection<ID> TemplateIds | Foundation | |
| ICollection<ID> Associations | Foundation | |
| ICollection<ID> ContentTypes | Foundation | |
| ICollection<ID> LastNameLetter | People Feature | |
| ICollection<ID> Offices | Offices Feature | |
| ICollection<ID> Schools | People Feature | |
| ICollection<ID> Titles | People Feature | |
| ICollection<Sort> Sort | Foundation | |
| ICollection<Facet> Facets | Foundation |
Sort:
| Name |
|---|
| SortBy SortBy |
| SortOrder SortOrder |
SortBy Enum:
| Name | Notes |
|---|---|
| Alpha | Handles people search sorting |
| Date | Handles insights search sort |
| Relevance | Handles site search sorting |
SortOrder Enum:
| Name |
|---|
| Ascending |
| Descending |
Facet Enum:
| Name |
|---|
| ContentType |
| LastNameLetter |
| Office |
| School |
| Title |
Putting the Pieces Together
The outline below indicates where the logic resides and is defined:
- Feature
- People
- Infrastructure
- Indexing
- FirstNameComputedField - Gets first name from Person Detail component.
- LastNameComputedField - Gets last name from Person Detail component.
- LastNameLetterComputedField - Computes last name letter from Person Detail component.
- SchoolsComputedField - Gets related schools from Education component.
- Providers
- PeopleCriteriaProvider : ICriteriaProvider
- PeopleIndexingProvider : IIndexingProvider
- PeopleResultProvider : IResultProvider
- PeopleSearchProvider : ISearchProvider
- Indexing
- Infrastructure
- Insights
- Infrastructure
- Providers
- InsightsCriteriaProvider : ICriteriaProvider
- InsightsIndexingProvider : IIndexingProvider
- InsightsResultProvider : IResultProvider
- InsightsSearchProvider : ISearchProvider
- Providers
- Infrastructure
- Offices
- Infrastructure
- Indexing
- OfficesComputedField - Gets related offices from Related Offices component
- Providers
- OfficesCriteriaProvider : ICriteriaProvider
- OfficesIndexingProvider : IIndexingProvider
- OfficesResultProvider : IResultProvider
- OfficesSearchProvider : ISearchProvider
- Indexing
- Infrastructure
- People
- Foundation
- Search
- Infrastructure
- Indexing
- AlphaSortComputedField - From IIndexingProvider(s)
- AssociationsComputedField - From IIndexingProvider(s)
- ContentTypeComputedField - From IIndexingProvider(s)
- DateSortComputedField - From IIndexingProvider(s)
- TitleComputedField - From IIndexingProvider(s)
- Providers
- ICriteriaProvider
- IIndexingProvider
- IResultProvider
- ISearchProvider
- Indexing
- Models
- Facet
- SearchFilter
- Sort
- SortBy
- SortOrder
- Services
- ISearchService - Interface for dependency injection.
- SearchService - Contains logic to assemble providers and execute search.
- Infrastructure
- Search
Summary
Hopefully this provides a good overview of a high level supporting search API design that has worked well for us. Please see part 2 in this series to see this plays into JSS. Coming Soon…